Scholars Gain New Data on Heavy Exotic Hadrons
As part of the Belle experiment, researchers were able to measure the energy dependence of e+e- -> B-anti-B, B-anti-B* and B*-anti-B* reactions in the 10.63 GeV to 11.02 GeV energy range for the first time. The new data will help clarify the nature of the group of exotic Upsilon mesons that have mass in this range. The results of the study were published in the Journal of High Energy Physics. Over 400 researchers have participated in the Belle experiment, including staff members of the HSE International Laboratory of Elementary Particle Physics.
The first Upsilon meson, consisting of b- and anti-b-quarks, was discovered in 1977. Its discovery also coincided with that of the heaviest b-quark, for which the authors of the study—American researchers Leon M. Lederman, Melvin Schwartz and Jack Steinberger—received a Nobel Prize in 1988.
In 2008, researchers discovered that high-energy Upsilon meson states have anomalous properties. The reason for these unexpected properties remains an unanswered question in hadron physics. Theoretical studies agree that there are additional degrees of freedom within these states: a pair comprising a lightweight quark and an anti-quark, or a valent gluon. Such multi-particle bound states are called ‘exotic hadrons’, and until recently, they had not been found. Additional experimental data was needed to distinguish various models of highly excited Upsilon meson structures. This data was collected during the Belle experiment in 2010 and serves as the foundation for the study published in the Journal of High Energy Physics.
The Belle detector was located at the collision point of KEK-B, an electron-positron collider in Japan, with the total beam energy close to 10 GeV. The detector collected data from 1999 to 2010. The main goal of the experiment was to study the properties of B+ and B0 mesons, consisting of a heavy anti-b-quark and one light u- or d-quark. A large number of rare decays of these particles was detected, and differences in the properties of particles and anti-particles (B+ and B-, B0 and anti-B0) were studied in order to uncover the mechanism behind the matter/anti-matter asymmetry of the contemporary universe.
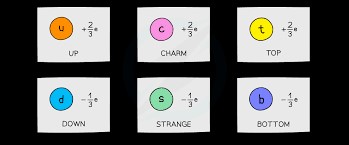
Quarks are elementary particles that form composite particles: baryons and mesons. Quarks have fractional electric charge values and are categorized in pairs in three generations in order of increasing mass: up and down, charm and strange, top and bottom.
A collision between an electron and a positron creates many particles which, in turn, interact or decay. In order to understand the reactions that occur after a particle collision, modern experiments consist of several layers of various detectors. Certain particles are registered and studied in these layers.
The Belle experiment used a silicon detector to determine the interaction point, a drift chamber to track the charged particles, and a caesium iodide-based counter for the photons.
Based on the scan data, the cross-section energy dependence for many reactions was measured. For example, a new heavy Upsilon(10750) meson was observed in the cross-sections of weakly excited Upsilon mesons produced together with a pair of pi+ and pi- mesons. Until recently, only the reactions that make a relatively small contribution to a total cross section were studied. Finally, the cross sections e+e- -> B-anti-B, B-anti-B* and B*-anti-B*, which make the largest contribution to a total cross section, were measured for the first time. This gave the researchers the first full set of data on exotic Upsilon mesons, which allowed several theoretical teams to start working to explain the measurements.

Roman Mizuk, Leading Research Fellow at the International Laboratory of Elementary Particle Physics
The data obtained includes some unexpected discoveries. The cross sections e+e- -> B-anti-B, B-anti-B* and B*-anti-B* demonstrate a complicated dependence on energy, which might provide some important information on the wave functions of exotic meson states. In the future, joint analysis of data on the energy dependence of the cross sections may help to shed light on the question of the structure of Upsilon mesons’ highly excited states.
Roman Mizuk
Leading Research Fellow, International Laboratory of Elementary Particle Physics
See also:
Russian Scientists Reconstruct Dynamics of Brain Neuron Model Using Neural Network
Researchers from HSE University in Nizhny Novgorod have shown that a neural network can reconstruct the dynamics of a brain neuron model using just a single set of measurements, such as recordings of its electrical activity. The developed neural network was trained to reconstruct the system's full dynamics and predict its behaviour under changing conditions. This method enables the investigation of complex biological processes, even when not all necessary measurements are available. The study has been published in Chaos, Solitons & Fractals.
Russian Physicists Discover Method to Increase Number of Atoms in Quantum Sensors
Physicists from the Institute of Spectroscopy of the Russian Academy of Sciences and HSE University have successfully trapped rubidium-87 atoms for over four seconds. Their method can help improve the accuracy of quantum sensors, where both the number of trapped atoms and the trapping time are crucial. Such quantum systems are used to study dark matter, refine navigation systems, and aid in mineral exploration. The study findings have been published in the Journal of Experimental and Theoretical Physics Letters.
Russian Scientists Demonstrate How Disorder Contributes to Emergence of Unusual Superconductivity
Researchers at HSE University and MIPT have investigated how the composition of electrons in a superconductor influences the emergence of intertype superconductivity—a unique state in which superconductors display unusual properties. It was previously believed that intertype superconductivity occurs only in materials with minimal impurities. However, the scientists discovered that the region of intertype superconductivity not only persists but can also expand in materials with a high concentration of impurities and defects. In the future, these superconductors could contribute to the development of highly sensitive sensors and detectors. The study has been published in Frontiers of Physics.
Scientists at HSE University Devise More Accurate Method for Predicting the Electrical Conductivity of Electrolyte Solutions
Researchers at HSE MIEM have developed a model for calculating the electrical conductivity of aqueous electrolyte solutions; for the first time, it considers the spatial distribution of ion charges instead of assuming their localisation at a single point. The model remains effective even at high electrolyte concentrations and across a wide temperature range. This breakthrough will contribute to the development of more efficient batteries and enable the calculation of electrical conductivity without the need for experimental testing. The study has been published in the Journal of Chemical Physics.
Russian Scientists Integrate Microdisk Laser and Waveguide on a Single Substrate
A group of Russian scientists led by Professor Natalia Kryzhanovskaya at HSE Campus in St Petersburg has been researching microdisk lasers with an active region based on arsenide quantum dots. For the first time, researchers have successfully developed a microdisk laser coupled with an optical waveguide and a photodetector on a single substrate. This design enables the implementation of a basic photonic circuit on the same substrate as the radiation source (microlaser). In the future, this will help speed up data transfer and reduce equipment weight without compromising quality. The study results have been published in Semiconductors.
First Successful Attempt in 55 years: Physicists in Russia and Germany Confirm 1969 Experiment Results
A team of researchers, with the participation of physicists from HSE University, replicated the 1969 experiment on superconductivity and its properties. The scientists induced superconductivity by deliberately deteriorating the interfaces between the layers of superconductors and ferromagnets in the system, resulting in better performance of spin valves compared to the classical version, where the interfaces between the layers are ideal. This approach could lead to the development of more efficient devices for data storage and computing. The study findings have been published in the Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology.
Russian Physicists Determine Indices Enabling Prediction of Laser Behaviour
Russian scientists, including researchers at HSE University, examined the features of fibre laser generation and identified universal critical indices for calculating their characteristics and operating regimes. The study findings will help predict and optimise laser parameters for high-speed communication systems, spectroscopy, and other areas of optical technology. The paper has been published in Optics & Laser Technology.
HSE Scientists Have Developed a New Model of Electric Double Layer
This new model accounts for a wide range of ion-electrode interactions and predicts a device's ability to store electric charge. The model's theoretical predictions align with the experimental results. Data on the behaviour of the electric double layer (EDL) can aid in the development of more efficient supercapacitors for portable electronics and electric vehicles. The study has been published in ChemPhysChem.
HSE Scientist Optimises Solution of Hydrodynamics Problems
Roman Gaydukov, Associate Professor at the MIEM HSE School of Applied Mathematics, has modelled the fluid flow around a rotating disk with small surface irregularities. His solution allows for predicting fluid flow behaviour without the need for powerful supercomputers. The results have been published in Russian Journal of Mathematical Physics.
Physicists from Russia and Brazil Unveil Mystery behind Complex Superconductor Patterns
Scientists at HSE MIEM and MIPT have demonstrated that highly complex spatial structures, similar to the intricate patterns found in nature, can emerge in superconductors. Mathematically, these patterns are described using the Ginzburg–Landau equation at a specific combination of parameters known as the Bogomolny point. The paper has been published in the Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter.


