Children with Autism Process Auditory Information Differently

A team of scientists, including researchers from the HSE Centre for Language and Brain, examined specific aspects of auditory perception in children with autism. The scientists observed atypical alpha rhythm activity both during sound perception and at rest. This suggests that these children experience abnormalities in the early stages of sound processing in the brain's auditory cortex. Over time, these abnormalities can result in language difficulties. The study findings have been published in Brain Structure and Function.
Autism spectrum disorders (ASD) are a group of conditions caused by abnormalities in brain development that can affect communication skills and social behaviour. Children with ASD often experience co-occurring language impairments, ranging from mild language deficits to a complete inability to speak.
The causes of language impairment in ASD are not yet well understood. Researchers believe that the neurobiological mechanisms of autism stem from an imbalance between excitatory and inhibitory processes in the cerebral cortex, driven by oscillations of nerve cells in the brain. These oscillations produce weak but detectable electromagnetic signals, such as alpha, beta, and gamma rhythms, which can be measured using magnetoencephalography (MEG).
An international team of researchers, including scientists from the HSE Centre for Language and Brain, studied alpha rhythm oscillations (markers of excitability) in children with autism. Alpha rhythms play a key role in processing sensory information and maintaining attention, eg during auditory perception.
The scientists explored the relationship between sound perception and language impairment in children with ASD. To achieve this, they used magnetoencephalography to measure brain activity in 20 children with autism of varying severity and in 20 typically developing controls. All study participants underwent clinical and behavioural language assessments, as well as tests for nonverbal intelligence (IQ) and the severity of autistic traits. Their language skills were measured using RuCLAB (Russian Child Language Assessment Battery). During the MEG, participants were presented with sound stimuli while their brain activity was measured, requiring no special actions from them. The authors of the experiment monitored alpha oscillations both at rest and during the processing of presented audio signals.
It was found that children with autism exhibit impaired alpha rhythms both during auditory perception and at rest. Typically, when sounds are processed in the auditory cortex, the power of alpha waves decreases significantly, while it increases during rest. The opposite pattern was observed in children with autism.
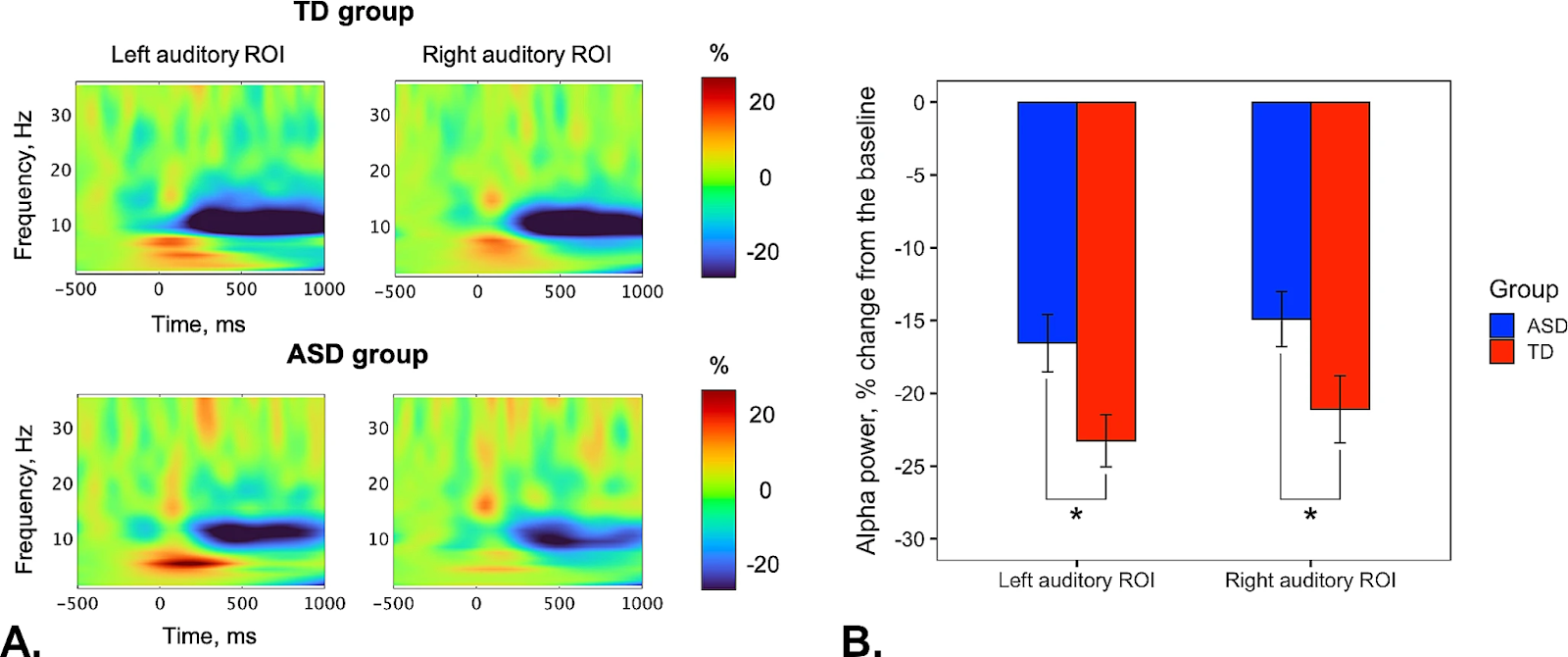
'A slight decrease in alpha rhythm power during auditory information processing in children with autism indicates increased excitability of neural networks in the auditory cortex, confirming an imbalance between excitation and inhibition in the cerebral cortex,' explains Vardan Arutiunian, co-author of the study and research fellow at the Seattle Children's Research Institute, USA.
The authors of the paper also found a link between brain activity at rest in the left auditory cortex and the language abilities of children with ASD. The researchers converted the complex, multidimensional MEG signals into a set of parameters, analysed them, and discovered that one component of the signal (offset), which reflects the average frequency of neural discharges, is associated with language skills. The higher this parameter (and consequently, the greater the resting neural excitability in the left auditory cortex), the poorer the language skills of children with ASD.

Olga Dragoy
'We analysed all the data collected during the experiment, including the MEG results, IQ tests, and assessments of autistic traits and language skills. It was found that children with more impaired neural processes in the left hemisphere exhibited poorer language abilities. We observed that in autism, abnormalities are present at the early stages of information processing in the auditory cortex, which can impact higher-level processes such as language,' according to Olga Dragoy, Director of the HSE Centre for Language and Brain.
The study's findings can lead to a better understanding of the causes of language impairment in autism spectrum disorders and contribute to the development of corrective interventions.
See also:
Machine Learning Links Two New Genes to Ischemic Stroke
A team of scientists from HSE University and the Kurchatov Institute used machine learning methods to investigate genetic predisposition to stroke. Their analysis of the genomes of over 5,000 people identified 131 genes linked to the risk of ischemic stroke. For two of these genes, the association was found for the first time. The paper has been published in PeerJ Computer Science.
First Digital Adult Reading Test Available on RuStore
HSE University's Centre for Language and Brain has developed the first standardised tool for assessing Russian reading skills in adults—the LexiMetr-A test. The test is now available digitally on the RuStore platform. This application allows for a quick and effective diagnosis of reading disorders, including dyslexia, in people aged 18 and older.
Low-Carbon Exports Reduce CO2 Emissions
Researchers at the HSE Faculty of Economic Sciences and the Federal Research Centre of Coal and Coal Chemistry have found that exporting low-carbon goods contributes to a better environment in Russian regions and helps them reduce greenhouse gas emissions. The study results have been published in R-Economy.
Russian Scientists Assess Dangers of Internal Waves During Underwater Volcanic Eruptions
Mathematicians at HSE University in Nizhny Novgorod and the A.V. Gaponov-Grekhov Institute of Applied Physics of the Russian Academy of Sciences studied internal waves generated in the ocean after the explosive eruption of an underwater volcano. The researchers calculated how the waves vary depending on ocean depth and the radius of the explosion source. It turns out that the strongest wave in the first group does not arrive immediately, but after a significant delay. This data can help predict the consequences of eruptions and enable advance preparation for potential threats. The article has been published in Natural Hazards. The research was carried out with support from the Russian Science Foundation (link in Russian).
Centre for Language and Brain Begins Cooperation with Academy of Sciences of Sakha Republic
HSE University's Centre for Language and Brain and the Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) have signed a partnership agreement, opening up new opportunities for research on the region's understudied languages and bilingualism. Thanks to modern methods, such as eye tracking and neuroimaging, scientists will be able to answer questions about how bilingualism works at the brain level.
How the Brain Responds to Prices: Scientists Discover Neural Marker for Price Perception
Russian scientists have discovered how the brain makes purchasing decisions. Using electroencephalography (EEG) and magnetoencephalography (MEG), researchers found that the brain responds almost instantly when a product's price deviates from expectations. This response engages brain regions involved in evaluating rewards and learning from past decisions. Thus, perceiving a product's value is not merely a conscious choice but also a function of automatic cognitive mechanisms. The results have been published in Frontiers in Human Neuroscience.
AI Predicts Behaviour of Quantum Systems
Scientists from HSE University, in collaboration with researchers from the University of Southern California, have developed an algorithm that rapidly and accurately predicts the behaviour of quantum systems, from quantum computers to solar panels. This methodology enabled the simulation of processes in the MoS₂ semiconductor and revealed that the movement of charged particles is influenced not only by the number of defects but also by their location. These defects can either slow down or accelerate charge transport, leading to effects that were previously difficult to account for with standard methods. The study has been published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
Electrical Brain Stimulation Helps Memorise New Words
A team of researchers at HSE University, in collaboration with scientists from Russian and foreign universities, has investigated the impact of electrical brain stimulation on learning new words. The experiment shows that direct current stimulation of language centres—Broca's and Wernicke's areas—can improve and speed up the memorisation of new words. The findings have been published in Neurobiology of Learning and Memory.
Artificial Intelligence Improves Risk Prediction of Complex Diseases
Neural network models developed at the HSE AI Research Centre have significantly improved the prediction of risks for obesity, type 1 diabetes, psoriasis, and other complex diseases. A joint study with Genotek Ltd showed that deep learning algorithms outperform traditional methods, particularly in cases involving complex gene interactions (epistasis). The findings have been published in Frontiers in Medicine.
Cerium Glows Yellow: Chemists Discover How to Control Luminescence of Rare Earth Elements
Researchers at HSE University and the Institute of Petrochemical Synthesis of the Russian Academy of Sciences have discovered a way to control both the colour and brightness of the glow emitted by rare earth elements. Their luminescence is generally predictable—for example, cerium typically emits light in the ultraviolet range. However, the scientists have demonstrated that this can be altered. They created a chemical environment in which a cerium ion began to emit a yellow glow. The findings could contribute to the development of new light sources, displays, and lasers. The study has been published in Optical Materials.


